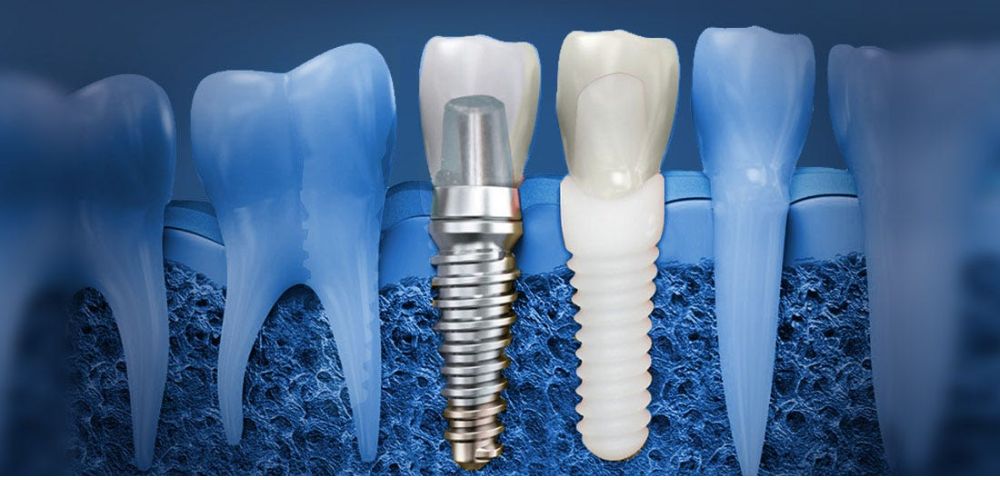
What Is a Dental Implant?
A dental implant is a small, biocompatible titanium post that is surgically placed into the jawbone. This post acts as an artificial tooth root, providing a sturdy foundation for a replacement tooth (crown), bridge, or denture. Over time, the implant integrates with the jawbone in a process called osseointegration, ensuring stability and durability similar to natural teeth.
How Dental Implants Work
1. Consultation & Examination
- Initial Assessment: Your dentist will evaluate your overall oral health, jawbone density, and suitability for the implant procedure.
- Imaging: X-rays or CT scans are often used to plan the implant placement accurately.
2. Surgical Placement
- Procedure: Under local anesthesia, the dentist surgically places the titanium post into the jawbone.
- Healing Time: The jawbone gradually fuses with the implant over several months, securing it firmly in place.
3. Abutment & Crown Placement
- Abutment Attachment: Once osseointegration is complete, a small connector called an abutment is attached to the implant.
- Final Restoration: A custom-made crown is then placed on the abutment, matching the color and shape of your natural teeth.
Benefits of Dental Implants
- Natural Look & Feel: Implants are designed to look and function like real teeth.
- Enhanced Function: They improve chewing, speaking, and overall comfort compared to removable dentures.
- Long-Lasting: With proper care, dental implants can last for decades, often a lifetime.
- Bone Health: Implants help preserve the jawbone and prevent bone loss that can occur when teeth are missing.
